Blog
Cloning Technology On The Rise, Humans Could Be Next
 Boyalife Group, a Chinese based company, believes that it has the technology necessary for human replication. The company is currently building the world’s largest cloning factory and is set to begin cloning cows later this year. The firm’s technology is so advanced that it could actually replicate humans as well. The only thing holding them from doing so is public perception.
Boyalife Group, a Chinese based company, believes that it has the technology necessary for human replication. The company is currently building the world’s largest cloning factory and is set to begin cloning cows later this year. The firm’s technology is so advanced that it could actually replicate humans as well. The only thing holding them from doing so is public perception.
The new cloning plant is under construction at the port of Tianjin, China. Production should begin at the plant within the next few months. The goal is to clone one million cows a year by 2020.
According to chief executive Xu Xiaochun, the group has its sights on cloning more than just cattle. The factory intends to produce thoroughbred racehorses and dogs as well. Furthermore, they will be partnering with a South Korean company along with the Chinese Academy of Sciences in an effort to improve their primate cloning capacity.
The next step after animals is to apply cloning technology on humans. “The technology is already there,” says Xu. “If this is allowed, I don’t think there are other companies better than Boyalife that makes better technology.”
The company is not currently engaged in human cloning activities, mostly because they fear a public backlash if they were to pursue it. But Xu contents that social values are subject to change, particularly in terms of people having more of a choice in reproduction.
“Unfortunately, currently, the only way to have a child is to have it be half its mum, half its dad,” said Xu. “You either have fifty-fifty, or you have a choice of having the genetics 100 percent from Daddy or 100 percent from Mummy. This is only a choice.”
Xu believes that cloning could be a safeguard of biodiversity with the Tianjin facility to house a gene bank that will be able to hold up to five million samples in liquid nitrogen. This would serve as a catalogue of endangered species allowing for the possibility of regenerating them down the road.
Timelapse Video of a Meteorite Exploding over the Mojave
Below you will find a beautiful timelapse of the Mojave Desert, shot and edited by astrophotographer Harun Mehmedinovic, that managed to capture a meteorite explosion.
MOJAVE BLUES from Harun Mehmedinovic on Vimeo.
3 Things That Could Change Our Lives
Researchers, scientists, and engineers from around the world are continuing to push the limits of what is possible. What these people are discovering have the potential to improve our lives in incredible ways. I have compiled three different stories that are each promising in their own right.
Here are three research stories that you should be aware of today:
Bionic Spinal Cord
Researchers in Australia have created a “bionic spinal cord” that they claim would give paralyzed people significant hope of walking again. What makes the device even more amazing is that it could actually be utilized through the power of thought, without the need for open brain surgery.
The researchers proof-of-concept results come from a study conducted on sheep, demonstrating high fidelity measurements taken from the region of the brain responsible for controlling voluntary movement with the use of the device.
Vertically Launching Electric Plane
Elon Musk has been a technology pioneer. Helping to build companies such as PayPal, Tesla, and SpaceX. Each of these companies has revolutionized (or are in the process of revolutionizing) their respective industries. Now, Musk has his sights on building an electric-powered plane.
During a Q&A session for the Hyperloop Pod ceremony, Musk was asked to tell the audience what his next big idea was. Musk’s response: “Well I have been thinking about the vertical takeoff and landing electric jet a bit more. I mean, I think I have something that might close. I’m quite tempted to do something about it.”
Can Our Minds Live Forever?
Scientists are looking to preserve a brain, along with all of its thoughts, memories, feelings and everything else that makes us who we are, even after we have passed. To accomplish “life beyond life,” they are looking to preserve a brain’s connectome. While they are still unsure about whether this is possible, the scientists are developing techniques that they believe will answer this question.
Kenneth Hayworth, a neuroscientist and the brainchild behind the Brain Preservation Technology Prize, believes that this technology will be possible. During an interview with Scientific America, Hayworth stated that he is “virtually certain that mind uploading is possible. Our best neuroscience models say that all these perceptual and sensorimotor memories are stored as static changes in the synapses between neurons.” This is exactly what the technique is designed to preserve.
Three Scientific Research Developments
We are only a few short weeks into 2016 and we already have a number of amazing new research breakthroughs. These new discoveries will likely have major impacts in both the medical and technological industries. Here are three scientific research developments that you should know about.
1) Cornell scientists confirm atoms will not move when someone is observing them
Cornell physicists proved that a quantum system cannot change while you are watching it. This effect was considered to be one of the oddest predictions of quantum theory, and the recent experiments confirmed it.
Mukund Vegalettore, assistant professor of physics, established Cornell’s first program to study the physics of materials cooled to temperatures as low as .000000001 above absolute zero. For the experiment, a group of graduate students created and cooled a gas of about a billion Rubidium atoms inside a vacuum chamber and suspended the mass between laser beams. It was during this experiment that the team noticed the atoms would not move around as long as they were under observation. The more often the group used a laser to measure the behavior, the less movement they were able to see.
This study has some fairly big ramifications, such as showing that quantum cryptography should actually work, meaning that an intruder can’t spy on your communications without destroying the data.
2) Scientists teach bacteria to perform artificial photosynthesis
Scientists have successfully induced Moorella thermoacetica, an originally nonphotosynthetic bacterium, to undergo photosynthesis in a hybrid artificial photosynthesis system for converting sunlight. The M. thermoacetica was coaxed to perform photosynthesis, even though it is naturally non-photosynthetic; the scientists essentially trained the bacteria to perform something that it was naturally genetically programmed to not do.
“We’ve demonstrated the first self-photosensitization of a nonphotosynthetic bacterium, M. thermoacetica, with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles to produce acetic acid from carbon dioxide at efficiencies and yield that are comparable to or may even exceed the capabilities of natural photosynthesis,” stated Peidong Yang, a chemist with Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division, who led the study.
3) Scientists develop sound wave that can manipulate stem cells without damage
A new class of sound wave has been developed for the first time in half a century. The sound wave was created by acoustics experts from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia. It is set to revolutionize the way that stem cells are used in medical treatments.
The new waves are known as “surface reflected bulk waves,” which are a combination of bulk sound waves and surface sound waves. Bulk sound waves cause objects to vibrate as one, while surface sound waves only cause the surface of the material to vibrate. The combination of these two waves is far more powerful than either of these waves alone.
As for the potential uses for this new sound wave? Well, it is able to break down liquids into an inhalable spray, paving the way for a wide range of drugs that can be delivered into the body without the need for pills or injections.
Scientists Locate “Missing Matter” In Universe

Ordinary matter, which makes up everything that we know — stars, planets, people — corresponds to five percent of the Universe. Only about half of this small percentage has actually been discovered; the other half has, until now, eluded scientists.
Numerical simulations have made it possible to predict that the rest of this ordinary matter should be located in large-scale structures that form the “cosmic web” at temperatures between 100,000 and 10 million degrees.
Scientists are the University of Geneva (UNIGE) in Switzerland have observed this phenomenon directly. Their research, recently published in Nature, shows that the majority of the missing ordinary matter is found in the form of a very hot gas associated with intergalactic filaments.
Galaxies are formed when ordinary matter collapses and then proceeds to cool down. In order to understand the origin of this formation, it is required to understand the form, as well as the location of the ordinary matter that we do not perceive (missing baryons) is located.
Astrophysicists from UNIGE and the Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) focused on Abell 2744, a massive cluster of galaxies with a complex distribution of dark and luminous matter at its core. The researchers observed this cluster with the XMM space telescope whose sensitivity to X-rays allows it to detect signatures of very hot gas.
Previous large-scale galaxy research has shown that the distribution of ordinary matter in the Universe is not homogenous, instead, it is concentrated into filamentary structures. These structures form a network of knots and links, referred to as the “cosmic web,” which connect to one another through filaments. Researchers were able to measure the temperature and density of these objects by focusing on the areas where they suspected to find these filaments.
“Now we must verify that the discovery of Abell 2744’s missing baryons is applicable to the entire universe. This will consist in studying these filamentary regions in detail, and measuring their temperature distribution and the various atoms that compose them, in order to understand how many heavy elements there are in the universe,” says lead scientist Dominique Eckert in the press release.
If you would like to learn more about this story, please check out this article.
Antarctica Experiencing Ice Gains
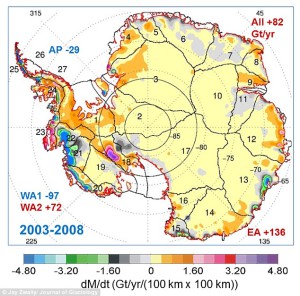 A new study conducted by NASA has revealed that Antarctica has actually seen more cumulative ice gains than it has seen losses.
A new study conducted by NASA has revealed that Antarctica has actually seen more cumulative ice gains than it has seen losses.
The study, led by Glaciologist Jay Zwally, shows that while the Antarctic Peninsula and parts of the West Antarctic continue to lose ice, the eastern side of the continent and interior of West Antarctica have recorded significant ice gains.
Furthermore, it has been determined that the ice caps are not actually contributing to the rising sea levels as much as scientists have originally thought.
These groundbreaking conclusions are based on new measurement methods that examine the height of the region’s ice sheet view satellites.
“The good news is that Antarctica is not currently contributing to sea level rise, but is taking 0.23 millimeters per year away,” Zwally stated. “But this is also bad news. If the 0.27 millimeters per year of sea level rise attributed to Antarctica in the IPCC report is not really coming from Antarctic, there must be some other contribution to sea level rise that is not accounted for.”

Until these discoveries were reported by NASA, it was believed that ice loss in Antarctica was the reason for the rise in global sea levels. Scientists believed that Antarctica was adding around 8% to global sea rise. The rising sea levels is a concern for many coastal cities around the world, such as Miami, where recent high tides have caused flooding.
If Jay Zwally’s study proves to be correct, it would mean that Antarctica is not contributing nearly as much to the increasing sea levels as originally thought.
Scientists may very well be underestimating the impact of other possible sources of rising sea levels, including melting from Greenland or the heating of the oceans.
If you would like to learn more about this discovery, please check out this article.
With The Discovery Of Water, Is Life Possible On Mars?

NASA and the world news has been buzzing since researchers discovered the best evidence yet that Mars does indeed have water on it. As the most similar to Earth of all the planets, it has many wondering: could life on Mars be a viable option?
As fresh and clean water becomes less and less available on earth (and extracting salt from water is still expensive), finding other sources of the most necessary ingredient to life is growing in importance.
With the knowledge of dried up riverbed and sedimentary rock formations, we were aware for a while of Mars’ watery past (most likely over a billion years ago), but it was assumed that it was in the past. Signs of erosion were examined, which helped determine that at one time Mars had oceans along its surface going over a mile deep. But this water source was depleted as the planet lost its protective magnetic field from strong solar wind.
Now equipped with imagery of the water formations along the mountains of Mars, it would seem possible to make it a harvestable place to grow vegetation for consuming, but there is a problem. The water is poisonous. It’s filled with perchlorates, which are lethal to humans, but the water can be treated and processed into drinking water. Since the discovery, researchers are wondering if there is a water spring or gusher still waiting to be found. With more knowledge, the possibilities could be endless.
This is just the beginning in learning how exactly humans can use Mars to solves some of her problems. According to Buzz Aldrin, who was the pilot of the first manned mission to the moon, this is another small step for mankind just like those first steps on the moon. He believes that, “no dream is too high for those with their eyes in the sky!”
Info courtesy of Forbes and Time.
New Discovery: Smallest Supermassive Blackhole Ever
Scientists have recently discovered the smallest supermassive blackhole to date. Using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers were able to spot the blackhole lurking in the centre of a dwarf galaxy.
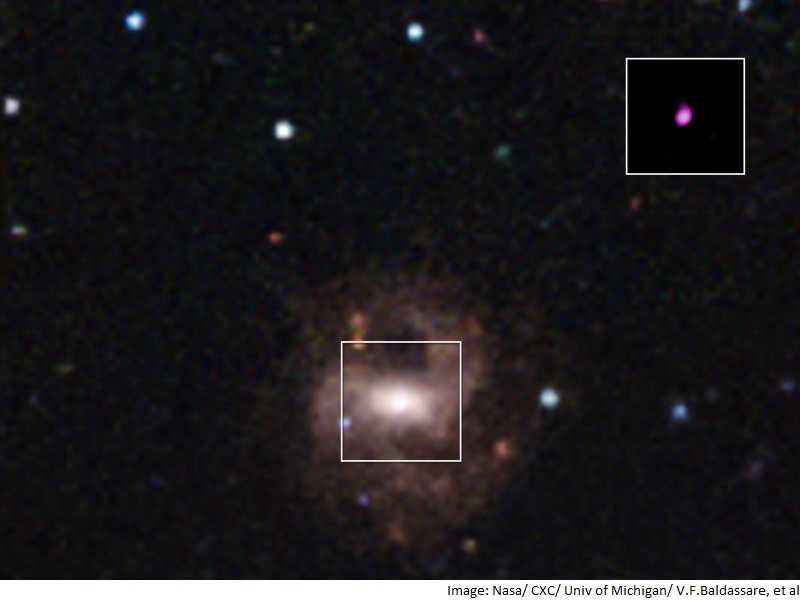

Located around 340 million light-years away from us, this blackhole is 50,000 times the mass of the sun. While this may sound large, when compared to the previous smallest object of its kind, this blackhole is actually two times smaller.
Supermassive blackholes are thought to form and evolve with the host galaxies whose centres they inhabit. Every large galaxy is believed to have a supermassive blackhole at its centre. This discovery, however, is the first supermassive blackhole found to be identified in a dwarf galaxy.
“By studying how galaxies like this one are growing and feeding their black holes and how the two are influencing each other, we could gain a better understanding of how galaxies were forming in the early universe,” said Vivienne Baldassare, a U-M doctoral student . “The black hole we found is active and based on the X-ray observations, it appears to be is consuming material at a rate similar to active black holes in much more massive galaxies.”
To learn more about this discovery and what it means for astronomers and researchers alike, check out this article.
NASA Mars Opportunity
NASA’s Mars Opportunity rover has been on Mars for 11 years and has covered a large distance during this time. 26.2 miles in fact, the distance of a marathon. The rover has captured amazing images and has allowed us to learn a great deal about the planet. To commemorate the event of Mars Opportunity rover completing a ‘marathon’ NASA has released a video that allows you to watch the entire journey it has taken throughout its mission to mars. It is a great video that gives you a amazing perspective of the planet. I highly recommend you take the time to check it out. Enjoy your trip to Mars!

